En el mundo del desarrollo moderno, los microservicios se han convertido en la arquitectura preferida para construir aplicaciones escalables y mantenibles. En este artículo, te mostraré cómo conectar tres microservicios utilizando dos tecnologías diferentes: Node.js y Spring Boot.
In the modern development world, microservices have become the preferred architecture for building scalable and maintainable applications. In this article, I'll show you how to connect three microservices using two different technologies: Node.js and Spring Boot.
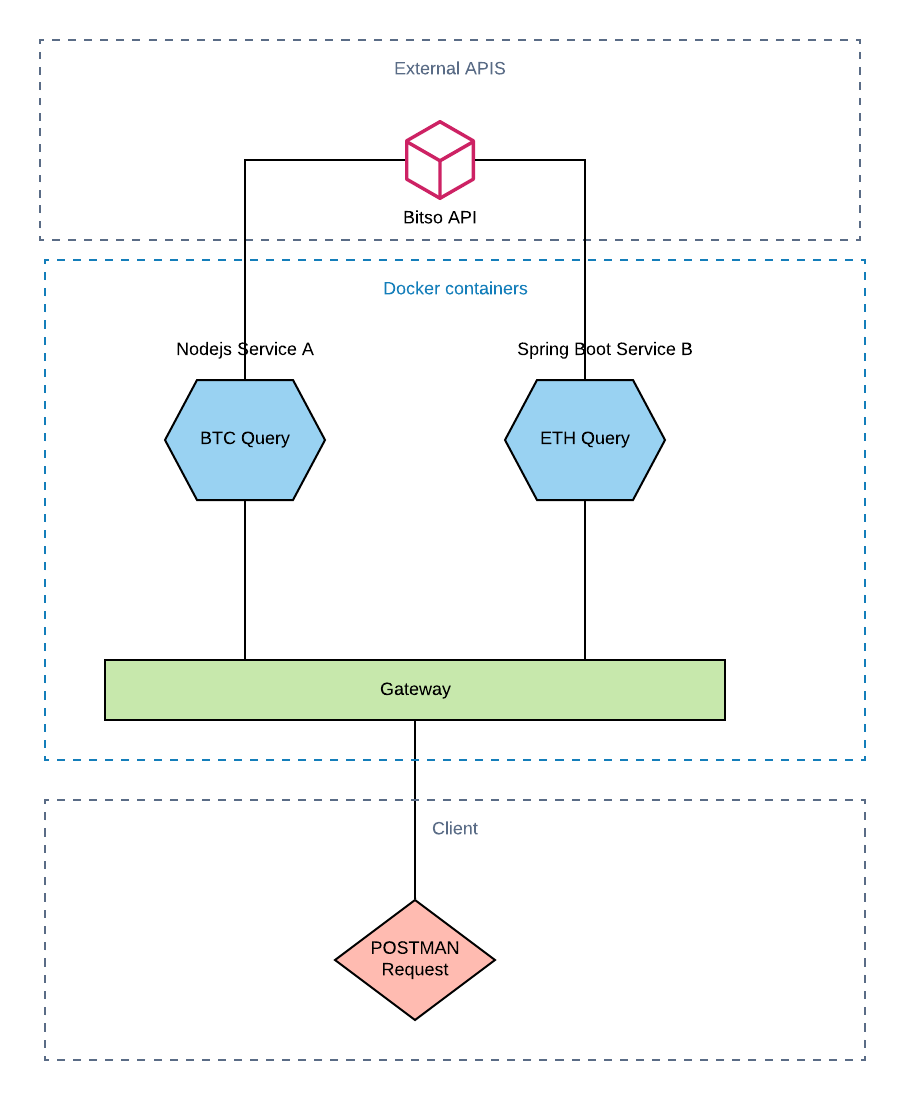
El objetivo es crear un sistema que consulte precios de criptomonedas en tiempo real utilizando la API de Bitso. La arquitectura consiste en:
The goal is to create a system that queries cryptocurrency prices in real time using the Bitso API. The architecture consists of:
- Servicio A (Node.js): Consulta el precio de Bitcoin (BTC)
- Servicio B (Spring Boot): Consulta el precio de Ethereum (ETH)
- Gateway (Node.js): Orquesta ambos servicios y unifica las respuestas
- Service A (Node.js): Queries the Bitcoin (BTC) price
- Service B (Spring Boot): Queries the Ethereum (ETH) price
- Gateway (Node.js): Orchestrates both services and unifies the responses
Además, containerizaremos todo con Docker para facilitar el despliegue y escalamiento en cualquier entorno de producción.
Additionally, we'll containerize everything with Docker to facilitate deployment and scaling in any production environment.
🔗 Código fuente: Ver repositorio completo en GitHub
🔗 Source code: View full repository on GitHub
📋 Contenido
📋 Contents
Servicio A: API de Bitcoin con Node.jsService A: Bitcoin API with Node.js
Comenzaremos construyendo el primer microservicio con Express.js, el framework más popular de Node.js para crear APIs REST. Este servicio se encargará exclusivamente de consultar el precio actual de Bitcoin.
We'll start by building the first microservice with Express.js, the most popular Node.js framework for creating REST APIs. This service will be exclusively responsible for querying the current Bitcoin price.
const express = require('express');
const axios = require('axios');
const app = express();
app.get('/btc', async (req, res) => {
try {
const response = await axios.get('https://api.bitso.com/v3/ticker/?book=btc_mxn');
res.json(response.data);
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: 'Error fetching BTC price' });
}
});
app.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('Service A running on port 3001');
});Dockerizando una Node.js appDockerizing a Node.js App
Para dockerizar nuestra aplicación de Node.js, necesitamos crear un Dockerfile que defina cómo construir nuestra imagen.
To dockerize our Node.js application, we need to create a Dockerfile that defines how to build our image.
FROM node:14-alpine
WORKDIR /app
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm install
COPY . .
EXPOSE 3001
CMD ["node", "index.js"]Servicio B: API de Ethereum con Spring BootService B: Ethereum API with Spring Boot
Para demostrar la interoperabilidad entre tecnologías, construiremos el segundo servicio con Spring Boot y Java. Este microservicio consultará el precio de Ethereum de forma independiente.
To demonstrate interoperability between technologies, we'll build the second service with Spring Boot and Java. This microservice will query the Ethereum price independently.
@RestController
public class EthController {
@GetMapping("/eth")
public ResponseEntity getEthPrice() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
String url = "https://api.bitso.com/v3/ticker/?book=eth_mxn";
return restTemplate.getForEntity(url, String.class);
}
}Containerización del servicio Spring BootContainerizing the Spring Boot Service
El proceso para containerizar una aplicación Spring Boot requiere primero compilar el proyecto y generar el archivo .jar, y luego crear el Dockerfile correspondiente:
The process to containerize a Spring Boot application requires first compiling the project and generating the .jar file, and then creating the corresponding Dockerfile:
FROM openjdk:11-jre-slim
COPY target/service-b-0.0.1.jar app.jar
EXPOSE 8080
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "/app.jar"]Gateway: El orquestador de serviciosGateway: The Service Orchestrator
El API Gateway es el punto de entrada único para los clientes. Su función es consumir ambos microservicios de forma paralela usando Promise.all() y devolver una respuesta unificada con los precios de ambas criptomonedas.
The API Gateway is the single entry point for clients. Its function is to consume both microservices in parallel using Promise.all() and return a unified response with the prices of both cryptocurrencies.
const express = require('express');
const axios = require('axios');
const app = express();
app.get('/prices', async (req, res) => {
try {
// Consultas paralelas para mejor rendimiento
const [btc, eth] = await Promise.all([
axios.get('http://service-a:3001/btc'),
axios.get('http://service-b:8080/eth')
]);
res.json({
btc: btc.data,
eth: eth.data,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
});
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: 'Error fetching prices' });
}
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('🚀 Gateway running on port 3000');
});Orquestación y escalamiento con Docker ComposeOrchestration and Scaling with Docker Compose
Docker Compose nos permite definir y ejecutar aplicaciones multi-contenedor. Con un solo archivo YAML podemos levantar toda nuestra arquitectura de microservicios:
Docker Compose allows us to define and run multi-container applications. With a single YAML file we can spin up our entire microservices architecture:
version: '3.8'
services:
service-a:
build: ./service-a
ports:
- "3001:3001"
restart: unless-stopped
service-b:
build: ./service-b
ports:
- "8080:8080"
restart: unless-stopped
gateway:
build: ./gateway
ports:
- "3000:3000"
depends_on:
- service-a
- service-b
restart: unless-stopped🎯 Conclusión🎯 Conclusion
Con esta arquitectura logramos varios objetivos clave del desarrollo moderno:
With this architecture we achieve several key goals of modern development:
- Desacoplamiento: Cada servicio es independiente y puede evolucionar por separado
- Escalabilidad: Podemos escalar horizontalmente cualquier servicio según la demanda
- Flexibilidad tecnológica: Usamos la mejor herramienta para cada tarea (Node.js y Java)
- Portabilidad: Docker garantiza que funcione igual en desarrollo y producción
- Decoupling: Each service is independent and can evolve separately
- Scalability: We can horizontally scale any service based on demand
- Technology flexibility: We use the best tool for each task (Node.js and Java)
- Portability: Docker ensures it works the same in development and production
Esta es la base sobre la cual puedes construir sistemas más complejos, agregando balanceadores de carga, service discovery, circuit breakers y más. ¡El límite es tu imaginación!
This is the foundation upon which you can build more complex systems, adding load balancers, service discovery, circuit breakers, and more. The sky's the limit!